의도
특정한 종류의 문제가 빈번하게 발생할 때 어떤 언어(패턴)으로 그 문제를 나타내어 표현하면 더 나은 경우가 있다고 한다.
어떤 언어에 대해 그 언어의 문법에 대한 표현을 정의하면서 그것을 사용하여 해당 언어로 기술된 문장을 해석하는 인터프리터를 함께 정의한다.
인터프리터는 문법을 정의하는 방법, 문법을 통해 문장을 구성하는 방법, 만든 문장을 해석하는 방법을 설명한다.
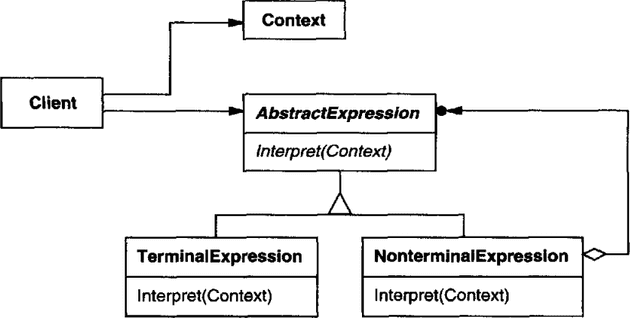
UML
AbstractExpression 추상 클래스는 Interpret() 즉, 주어진 표현(Context)을 해석하는 메서드를 정의하고 있다.
TerminalExpression은 특정 문법을 통해 Context를 해석하도록 Interpret()를 구현한다.
NonterminalExpression은 다수의 문법을 통해 해석하는 Interpret()를 구현한다. 이 때 AbstractExpression을 참조하기 때문에 다른 인터프리터를 조합한 구조를 통해 Context를 해석할 수 있다. 이는 컴포지트 패턴이므로 인터프리터는 트리 구조를 갖게 된다.
사용 시기
- 정의할 언어의 문법이 간단한 경우. 복잡하다면 인터프리터 대신 parser를 쓰는게 훨씬 낫다.
- 효율성을 따지지 않을 때.
장점
기존에 정의된 클래스를 상속받아 재정의하거나 새로운 서브 클래스로 확장하여 문법을 변경할 수 있다.
단점
복잡한 문법을 표현해야한다면 유지보수하기 힘들다.
구현
같은 간단한 덧셈 연산을 나타내야한다고 하자.
class Operator {
public:
virtual int interpret();
}어떤 수식이 주어졌을 때 그걸 해석하는 인터페이스를 만든 후 서브 클래스에서 어떤 문법을 나타내어 해석하도록 구현한다.
class AddOperator : public Operator {
public:
MultiplyOperator(Operator* operatorA, OperatorB* operatorB) :
_operatorA(operatorA), _operatorB(operatorB) { }
virtual int interpret() {
return _operatorA->interpret() + _operatorB->interpret();
}
private:
Operator* _operatorA;
Operator* _operatorB;
}
class IntegerOperator : public Operator {
public:
IntegerOperator(int n) : _n(n) { }
virtual int interpret() {
return n;
}
private:
int n;
}실 사용은 이렇게 할 수 있다.
IntegerOperator* a = new IntegerOperator(3);
IntegerOperator* b = new IntegerOperator(4);
AddOperator* add = new AddOperator(a, b);
add.interpret(); // return 3+4만약 정수 4개를 연산하도록 만들어야 한다면 이렇게 할 수 있다.
IntegerOperator* a = new IntegerOperator(3);
IntegerOperator* b = new IntegerOperator(4);
IntegerOperator* c = new IntegerOperator(1);
IntegerOperator* d = new IntegerOperator(5);
AddOperator* AB = new AddOperator(a, b);
AddOperator* CD = new AddOperator(c, d);
AddOperator* add = new AddOperator(AB, CD);
add.interpret(); // return (3+4) + (1+5)또한 Operator의 서브 클래스가 여러 Operator를 가지도록 만들 수도 있다.
class MultpleAddOperator : public Operator {
public:
MultipleAddOperator(list<Operator*> operatorList) : _operatorList(operatorList) {}
virtual int interpret() {
int result = 0;
for(auto iter = operatorList.begin(); iter != operatorList.end(); iter++) {
result += operator.interpret();
}
return result;
}
private:
list<Operator*> _operatorList;
}이 서브 클래스는 여러 operator를 리스트로 관리하면서 모든 Operator의 연산 결과를 더해 반환하도록 하고 있다.
인터프리터는 컴포지트 패턴을 사용하고 있지만, 단 하나의 문법을 나타내기 위해 사용할 때만 인터프리터라고 한다.